To start capturing network packets, select WiFi sniffer on the tool bar, or AirPCap sniffer if you have an AirPCap adapter. You must have the drivers installed; read NDIS driver installation for more details.
As for adapter compatibility, it depends on the corresponding adapter's drivers quality. In brief:
•Most Alfa adapters (like AWUSS036H) are compatible
•Most Intel adapters (used in many laptops) are incompatible
•Mixed results with TP-Link adapters: they usually works best with the drivers supplied by the chipset vendor rather than TP-Link; the ones we have tested and confirmed working are TL-WN7200ND, TL-WN822N, TL-WN722
•Atheros: mostly compatible (tested: AR9002WB, AR9485, AR5BW222, AR56x), but there are different problems with some specific specific adapters (e.g. not capturing the packets or even BSOD)
There is no 'golden rule'. Even generic noname adapters may work correctly if you can find a stable driver that does not cause the program (or the system) to fail.
Once the drivers for the adapter and NDIS drivers are installed, select the correct device (for AipPCap adapters, it is typically listed as \\.\airpcap00 device) and channel and press [OK]. If you're unsure about the channel, press [Detect networks], and the program will start monitoring all channels; you can press Save at any time to save the list of available networks:
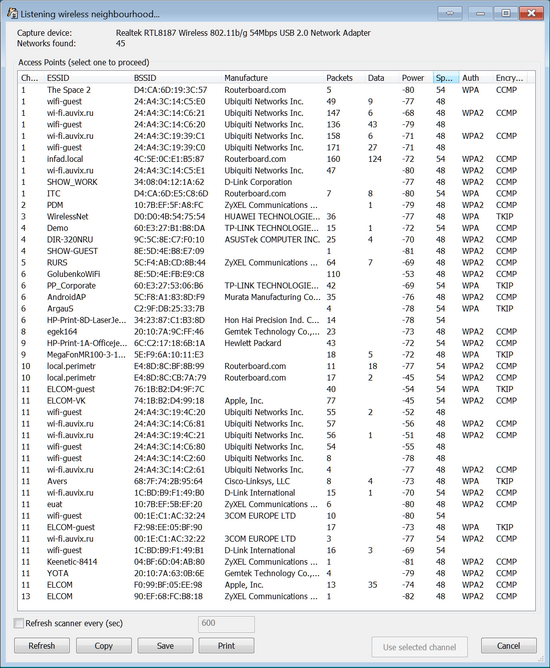
Select an access point and press Use selected. The program will start monitoring the selected channel across all wireless networks in range. You can also monitor several channels at once by pressing Multiple. In this case, the program will monitor all channels one after another. Do note that, if you use this option, you could miss proper handshakes on currently inactive channels while the program monitors another channel.
Once the handshake packets are captured, they are shown in the program:
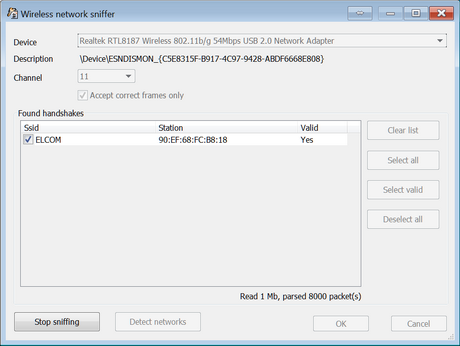
All captured packets can be mirrored into a pcap-file (for further analysis in third-party software). If that option is enabled, protection from lost handshakle packets is enabled automatically.
Please note that some adapters may work correctly only if the Accept correct frames only option is turned off.
Once you get the handshake, press Stop sniffing and OK. Now you can start the recovery process. Note that if you're using a trial or Standard edition, the packets will be captured, but you will not be able to import them for further password recovery; this feature is available in the Professional edition only (for more details, see Limitations of unregistered version and Registration).
If you don't have a compatible wireless adapter, there are alternative ways to import the required data. tcpdump is a common packet sniffer that allows the user to intercept and display TCP/IP and other packets being transmitted or received over a network to which the computer is attached. It was originally written by several people working in the Lawrence Berkeley Laboratory; now distributed under a permissive free software licence, and works on most Unix-like operating systems. There are also ports of tcpdump for Windows.
Examples of existing packet sniffers that can export packets in the tcpdump format: airodump-ng, OmniPeek.
The captured data should contain the full authentication handshake from a real client and access point. Please note that the program does not work with packets where linktype is LINKTYPE_ETHERNET (they come from wired, not wireless networks).